内存和地址
首先要从内存和地址开始讲起。在我们眼里,内存和地址就像下图一样,很直观。
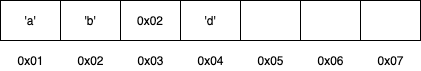
我们直觉上,上面的图应该就对应下面的代码。
char a = 'a';
char b = 'b';
char* c = &b;
char d = 'd';
但是,为什么呢? 为什么第三个位置上的0x02 就因为它长的像一个地址,我们直觉上就是将它归为地址呢?
把它解释为一个字符 值不行吗?就像
char a = 'a';
char b = 'b';
char c = 0x02;
char d = 'd';
也行!所以不能只看内存中的数据就做出判断,况且如果看到真实内存中的十六进制表示时,我们估计连猜的欲望都没有了。 所以,一切由代码决定,而最终解释权则在编译器手里。
一个简单的强制类型转换例子
int simple_exam() {
int a = 1;
int* p_a = &a;
long cast_long = (long) p_a;
printf("size of pointer: %lu, size of long: %lu\n", sizeof(p_a), sizeof(cast_long));
printf("p_a value: %p, cast_long value: %lu\n", p_a, cast_long);
/* output:
size of pointer: 8, size of long: 8
p_a value: 0x7ffee34cb8ec, cast_long value: 140732711876844
*/
return 0;
}
上面,我们将一个指针强制转换为了long 类型,编译器觉得没问题(0x7ffee34cb8ec 对应十进制数就是140732711876844 )。
其实这个例子没什么多大的现实意义,谁会将一个指针值转换为一个未知的整数呢?当然,在随机数生成上可能有用。
Whatever,我举上面的例子主要是想说明,编译器对于合法的语句,就是“机械”的进行翻译,不管是指针还是常量,
编译器看到的都只是内存中的一串二进制数,编译器就是按照你写的代码进行解释
(这个例子中,编译器将0x7ffee34cb8ec 解释为了140732711876844)。
结构体的强制类型转换
typedef struct Ping{
int a;
char b;
} Ping;
typedef struct Pong{
char a;
int b;
} Pong;
int cast_struct() {
Ping ping = {98, 'a'};
Ping *p_ping = &ping;
Pong *p_pong = (Pong *)p_ping;
printf("size of struct Ping: %lu, struct Pong: %lu\n", sizeof(Ping), sizeof(Pong));
printf("ping address: %p, p_ping value: %p, p_ping value: %p\n", &ping, p_ping, p_pong);
printf("Ping->a: %d, Ping->b: %c\n", p_ping->a, p_ping->b);
printf("Pong->a: %c, Pong->b: %d\n", p_pong->a, p_pong->b);
/* output:
size of struct Ping: 8, struct Pong: 8
ping address: 0x7ffee4e888c8, p_ping value: 0x7ffee4e888c8, p_ping value: 0x7ffee4e888c8
Ping->a: 98, Ping->b: a
Pong->a: b, Pong->b: 97
*/
return 0;
}
上面程序的内存视图就像:
address 内存中的数据
0x00007ffee4e888b8 | c8 88 e8 e4 fe 7f 00 00 // p_ping
0x00007ffee4e888c0 | c8 88 e8 e4 fe 7f 00 00 // p_pong
0x00007ffee4e888c8 | 62 00 00 00 61 00 00 00 // ping
结构体Ping Pong 由于数据对齐,所以长度都是8字节。
Pong *p_pong = (Pong *)p_ping;
这行使得编译器将原来Ping 内的数据强制解释为Pong 中对应类型的数据。这里 int 98 就转换成了char 'b',
同理,char 'a' 转换成了int 97。
实现一个多态
typedef struct man {
char *name;
int age;
struct profession *prof;
} Man;
typedef void (*printfunc)(Man *);
typedef struct profession {
const char *prof_name;
// 可以添加职业特定的动作
printfunc introduce;
} Profession;
typedef struct programmer {
char *name;
int age;
struct profession *prof;
// 可以添加程序员相关的各种属性
int is_bald;
} Programmer;
typedef struct researcher {
char *name;
int age;
struct profession *prof;
// 可以添加研究员相关的各种属性
char *direction;
} Researcher;
void programmer_introduce(Man *self) {
Programmer *programmer = (Programmer *)self;
printf("My name is %s, %d years old, and work as a %s.",
programmer->name, programmer->age, programmer->prof->prof_name);
printf((programmer->is_bald == 1) ? ":(\n": ":)\n");
}
Profession PythonDev = {
"Python Develop",
programmer_introduce,
};
void researcher_introduce(Man *self) {
Researcher *researcher = (Researcher *)self;
printf("My name is %s, %d years old, and work as a %s.",
researcher->name, researcher->age, researcher->prof->prof_name);
printf("My research direction is %s.\n", researcher->direction);
}
Profession MatchResearch = {
"Math Research",
researcher_introduce,
};
int polymorphism() {
Man *a, *b;
Programmer hstk = {"hstk", 25, &PythonDev, 0};
Researcher hstk30 = {"hstk30", 30, &MatchResearch, "Math"};
a = (Man *)(&hstk);
b = (Man *)(&hstk30);
a->prof->introduce(a);
b->prof->introduce(b);
/* output:
My name is hstk, 25 years old, and work as a Python Develop.:)
My name is hstk30, 30 years old, and work as a Math Research.My research direction is Math
*/
return 0;
}
上面的代码就像实现了下面的继承关系。
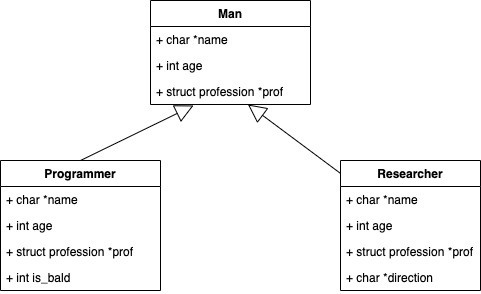
上面的关键就Man 和Programmer,Researcher 的前三个字段相同,所以在强制类型转换a = (Man *) (&hstk) 后,
我们能像正常使用Man 一样,使用这个转换后的数据。并且相同的代码,出现了不同的行为。
一个Linux 中的高级用法
typeofis a compiler extension(GNU). In a nutshell it’s a convenient way to declare an object having the same type as another. For example:
int x; /* Plain old int variable. */
typeof(x) y; /* Same type as x. Plain old int variable. */
It works entirely at compile-time and it’s primarily used in macros. One famous example of macro relying on typeof is container_of.
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
*
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
总结
就是这么简单。这也是C语言 的主要特点和优势,通过指针直接操纵内存数据,而在写Python 时,基本上就没有内存这个概念。
来自《深入理解计算机系统》3ed 补充
强制类型转换运算符可以将一种数据类型转换为另一种。因此,强制类型转换
(byte_pointer) &x表明无论指针&x以前是什么类型, 它现在就是一个指向数据类型为unsigned char的指针。这里给出的这些强制类型转换不会改变真实的指针, 它们只是告诉编译器以新的数据类型来看待被指向的数据。